The market offers a wide array of liquid membranes, available in various application forms such as spraying, rolling, or trowelling. These liquid membranes come in diverse types, including water or acrylic-based, polyurethane, silicone, bituminous, cementitious, polyurea, polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), epoxy, or combinations thereof. It’s worth noting that there are likely other types not covered in this discourse, but the fundamental principles for their installation typically remain consistent.While the installation of liquid membranes may seem straightforward for waterproofing purposes, it is imperative to give meticulous attention to the substrate type and condition. The following key points should be carefully considered during the installation process:
 1. Substrate Dryness: Adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the required level of substrate dryness specific to the type of membrane being used is of paramount importance.
1. Substrate Dryness: Adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the required level of substrate dryness specific to the type of membrane being used is of paramount importance.
2. Moisture Absorption: Assess whether the substrate is susceptible to absorbing moisture from the opposing side, which could potentially lead to delamination. In such cases, alternative systems or breathable membranes should be contemplated.
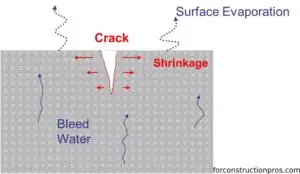 3. Concrete Maturity: Prior to applying the liquid membrane, it is critical to confirm that the concrete has reached a minimum age of 56 days. Although manufacturers often recommend a minimum of 28 days, it is essential to recognise that concrete continues to dry and shrink for a considerable period beyond this timeframe.
3. Concrete Maturity: Prior to applying the liquid membrane, it is critical to confirm that the concrete has reached a minimum age of 56 days. Although manufacturers often recommend a minimum of 28 days, it is essential to recognise that concrete continues to dry and shrink for a considerable period beyond this timeframe.
4. Crack Identification and Treatment: Identify static cracks and attend to any active ones by rectifying the root cause or incorporating bond breakers across the cracks.
5. Surface Levelling: Address any high and low points to ensure consistent membrane thickness throughout the application.
6. Substrate Falls: Providing proper falls to the substrate is essential, as liquid membranes do not perform optimally on flat surfaces. It is highly advisable to apply the membrane directly onto the sloped structural element rather than on a screed, which is inclined to delaminate and draw moisture through the joints in the event of bond failure.

7. Substrate Preparation: Ensure that the substrate is prepared to the manufacturer’s recommended Concrete Surface Profile (CSP) level.
8. Primer Application: Use a compatible primer before applying the liquid membrane, or opt for a self-priming solution.
9. Product Selection Criteria: Select the appropriate product by evaluating factors such as full elongation before break, modulus of elasticity, plasticity, tensile strength, UV resistance, traffic suitability, and chemical resistance.
10. Membrane terminations: When the membrane returns up, down, or finishes flat, it is imperative to terminate approximately to prevent water from reaching the membrane ends, thus causing delamination.
It is important to note that the recommendations provided above are based on our professional opinion, stemming from our experience in the field of waterproofing, concrete repairs, and concrete technology. The thorough consideration of these factors is crucial in ensuring the successful installation and performance of liquid membranes in various applications.
Written by:
Hacene Baleh
28/07/2024














